Hydrogène vert dans l’industrie
Green hydrogen is a clean and renewable energy source that is revolutionizing the industry. By using renewable energy to produce hydrogen from water, this technology offers an alternative to fossil fuels, thereby reducing carbon emissions and contributing to the fight against climate change. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which green hydrogen is produced, stored, and used in the industry, as well as its economic and environmental benefits. We will also discuss current challenges and future opportunities for this emerging technology.
I. Context on the urgency to reduce carbon emissions in the industry
As in many sectors, it is urgent to reduce carbon emissions in the industry.
Industry is one of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases in the world, responsible for about one third of total CO2 emissions. Energy production, transportation, agriculture, manufacturing industry, chemical processes, and construction materials are the main contributors to these emissions.
Climate change is a growing threat to the planet, manifested in extreme weather events, glacier melting, sea level rise, and disruption of ecosystems. To limit the impacts of climate change, it is urgent to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and the industry must take an active part in this transition.
Governments worldwide have started to take action to limit industry’s carbon emissions by imposing stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions and encouraging the adoption of cleaner and more efficient technologies. However, these efforts will not be sufficient to achieve global emission reduction goals.
This is why many companies are seeking alternative solutions to reduce their carbon emissions, including adopting renewable energy production technologies, improving the energy efficiency of their processes, and investing in innovative technologies such as green hydrogen.
Green hydrogen in the industry is a promising solution to reduce carbon emissions in this sector. By producing hydrogen from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydraulic energy, green hydrogen can offer a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels for energy production and industrial processes.
II. What is green hydrogen?
What exactly is green hydrogen? Production, manufacturing…
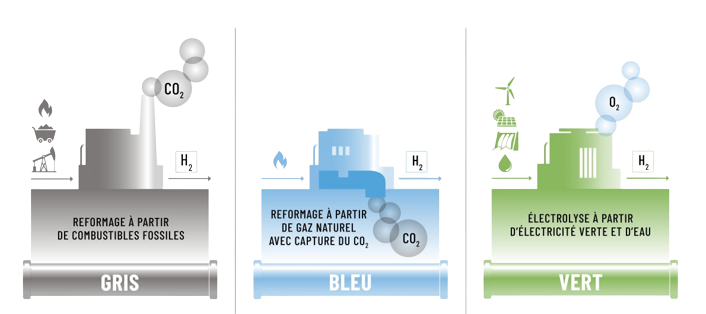
This type of hydrogen, as there are several, is produced from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydraulic energy, which do not produce greenhouse gases. Unlike gray or blue hydrogen, which are produced from fossil energy sources such as natural gas, green hydrogen has an extremely low impact on the environment.
Two methods exist to produce green hydrogen: water electrolysis and biomass gasification.
Method 1: Water Electrolysis
Water electrolysis is the process of separating the basic components of water, hydrogen and oxygen, using an electric current to “split” water molecules. The source of electricity to perform this action comes from solar or wind energy.
Method 2: Biomass Gasification
Biomass gasification is a process of converting organic matter (compost, animal waste, organic waste, etc.) into synthetic gas (or syngas): a basis for producing hydrogen. In this process, organic matter is heated to high temperatures in the presence of a gasifying agent, such as steam or oxygen. The organic matter then decomposes into gas, which is then processed to separate the hydrogen.
At the moment, one of the drawbacks lies in the rather high cost of green hydrogen production compared to other types of hydrogen, which are less sustainable.
However, this alternative remains an interesting avenue in the context of the environmental transition of industries.

III. Presentation of green hydrogen as a promising solution
Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe and can be produced from various green and less green energy sources.
Its applications are numerous:
- Powering industrial processes,
- Operating vehicles and equipment without greenhouse gas emissions,
- Storing or transporting it for “on-demand” energy use at different sites, for example
- Powering fuel cells for electric vehicles, buildings, data centers, or other equipment, providing a clean and efficient alternative to traditional combustion systems.
IV. The benefits of green hydrogen in the industry
Here are the main benefits of using green hydrogen in the industry:
- Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions: One of the main advantages of green hydrogen is that it significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions in the industry. As mentioned earlier, it is produced from renewable energy sources: therefore, its production causes minimal greenhouse gas emissions (It cannot be said that they are zero since the manufacturing of renewable energy-producing infrastructures itself emits greenhouse gases). It can be a relevant lever in the objective of reducing CO2 emissions and moving towards carbon neutrality.
- Versatility: Green hydrogen can be used in a wide variety of applications and industrial sectors: heat and electricity production, fertilizer production, chemical manufacturing.
- Energy storage: Its ability to be stored is its main asset: it allows for time-shifting, anticipation, and responsiveness when other energy sources are not available.
- Performance: In the case of use to power fuel cells, its efficiency will be higher than that of internal combustion engines. Its use can therefore help industries improve their energy efficiency and reduce their volume of fossil energy consumption.
- Noise and odor reduction: The use of green hydrogen can also help reduce the noise and odors associated with industrial processes. Unlike fossil fuels, hydrogen produces neither noise nor smoke: considerable advantages considering the sometimes observed working conditions in the industry.
V. The applications of green hydrogen in the industry
In this section, we will explore the various applications of green hydrogen in the industry.
- Electricity production: Green hydrogen can be used to produce electricity in power plants. Fuel cells can convert hydrogen into electricity, thus generating clean energy.
- Heating and cooling: These are two processes commonly used in the industry. Hydrogen boilers can replace natural gas boilers for building heating. Absorption refrigerators can also be powered by hydrogen, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Transport: Vehicles powered by green hydrogen can provide a clean and efficient alternative to traditional vehicles, trains, and ships using fossil fuels, especially for transporting goods and raw materials.
- Chemical industry: Production of basic chemicals such as ammonia, methanol, and others.
VI. Future prospects of green hydrogen in the industry
In this final part of the article, we will explore the future outlook of green hydrogen in the industry.
Increase in production: As the demand for green hydrogen rises, its production costs continue to decrease. Simultaneously, more and more companies and governments are adopting carbon neutrality goals, encouraging initiatives towards diversifying energy sources.
Growing demand: Industries require sustainable solutions to meet their greenhouse gas emission reduction targets, and green hydrogen offers a promising solution. The demand is expected to continue growing in the years to come.
Development of new markets: Industries are increasingly recognizing the opportunities presented by green hydrogen, both in terms of environmental impact and financial gains in certain areas.
In conclusion, green hydrogen offers numerous promising prospects for the industry. Its manufacturing process is constantly evolving, making this solution increasingly competitive compared to fossil fuels. Its advantages in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions, versatility, energy storage, performance, and noise and odor reduction make this energy source a key solution for achieving carbon neutrality goals.